
The traditional professional services industry will likely be radically different in ten years. Changing clients’ demands, employee expectations, rapid technology developments, and other external factors will change the nature of jobs and skills required in the future. Ultimately, these factors, with technology in the lead, may even challenge the very nature of the “practical expertise” that professionals deliver.
An Age of Disruption
Many industries and business models are at risk of being disrupted due to rapid technological developments, enabling new business models, replacing old distribution channels, and changing the way people and businesses interact with each other.
At this moment we see groundbreaking disruption taking place across most industries. When you take a look at the Fortune 1000 over the last 40 years, starting from 1973 you see that major changes have taken place. By 1983, one-third of these companies have fallen off the list. By 2013, only 30% of the original companies are still on the list. This pace of change will continue to increase as only a third of today’s major companies are expected to survive the next 25 years.
These changes are driven by megatrends that have far-reaching, interrelated consequences for business, economies, industries, societies, and individuals. Combined they are causing massive transformational shifts.
Digital technology developments are the leading disrupter, fed by social, mobile, cloud, big data, artificial intelligence, and growing demand for “anytime-anywhere” access to information. Other causes include changing global demographics; increase entrepreneurship and innovation, which close the gap between mature and developing economies; and the movement of economic centers from West to East and North to South.
Professional services like accounting, legal and consulting have so far not been highly impacted by these technological developments, but all signs are there that real change is coming and that the industry is at the gates of a digital transformation process. The biggest impact might not just come from new ways of organizing and delivering professional services, but also the very nature of the “practical expertise” that professionals deliver are being challenged.
But first, take a step back!
Then join our niche Job Board with a 100% Professional Services focus. With 1-click you reach:
- 150+ Job Boards and 2.000+ Publisher Sites.
- 50+ million Job Seekers.
- Get at the top of 30+ million daily email alerts send to Job Seekers.
- Jobs are also posted to Google for Jobs, reaching millions of Job Seekers who search for Jobs on Google every day.
Learn more about our Job Posting options or Post a Job straightaway on our niche Job Board for the Professional Services sector only.
Why do Professional Services Exist?
Ongoing specialization has been a decisive factor for the current state of our society. The effects of specialization is such a broad concept that it touches upon almost everything in our daily life. And our natural urge for specialization is also one of the main reasons why professional services exist. Society and businesses cannot know everything and therefore need specialists with practical experience to help and guide us.
Historically, technology developments changed the course of our specialization in important ways. Now everything points to the fact that technology is to drastically change the way we actually use professional services. Some even think that technology will eventually replace these service providers because technology enables more efficient ways of knowledge sharing, which is the core of professional services.
Main Sectors Impacted
Professional services are a major part of the overall economy, especially in the Western world, whereby it is a fast-growing sector in the rest of the world. So it is likely that any change will have a considerable impact on our economies, let alone what a drastic change in the professional services industry will mean.
At the level of the professional services industry, in general, there will be an increasing skill shortage and it will be more difficult to find the right person for the job. It is also expected that medium-sized firms are likely to face the biggest challenges, especially at the level of compliance-related services. Some expect that mainly the bottom part of the professional services pyramid will be impacted. Technology will replace much of the hard work of discovery, analysis, and comparison of information which is mainly done at the low end. Furthermore, low-end services can be replaced by self-service platforms or will become commoditized services, especially when technology enables direct tapping into the flows of client data as needed for instance for accounting and audits.
Accounting firms and professionals will face new challenges caused by new technology, new platforms, new services, and changing customer expectations. Some services may be automated, commoditized, or will be done in-house by the client itself due to new technological ways for clients to make sense of their own financial data, which data, in the end, is not much more than a registration of its business transactions.
Post your job on our Niche Job Board for the Professional Services Sector.
While the legal profession went through some changes in recent decades, major changes are expected across the legal industry over the next ten years. The transformation of the legal industry will likely be radical due to rapid technological developments, shifts in global workforce demographics, changing client demands, and the need to offer clients more value for money. Within four years a tipping point is expected for individual firms that will impact the competitive landscape and the role of talent.
For the consulting profession, the same external factors as for accounting and legal will have an effect on the shape and form of the consulting industry. However, part of the consulting industry may also benefit from this disruption age. As a result of the disruption, clients are rethinking their own purpose and business models. Therefore, there will be an increased demand for technology-based strategy consulting and this will likely go hand-in-hand with new parties entering into strategy consulting.
Main Causes and Disruptors
Increased Competition – Enormous increase in competition is expected as new players enter the market or alternative business structures are being used. Examples include:
- What you already see happening is that traditional accounting firms are entering the legal and consulting market as their core audit market sees signs of turbulence, with increasing price pressure and a growing readiness to look beyond the usual suspects for this kind of work.
- The growing importance of competitors from emerging markets. Mainly the top US and UK firms have benefited from globalization, however, large firms from emerging markets are creating serious activities in their own countries and western markets.
- Private equity-backed commercial law firms challenging the traditional partner based law firms.
- Other recent new business models applied to the legal market include Elevate, Conduit Law, and Lawyers on Demand.
Deregulation – The increasing trend of deregulation will reduce restrictions on almost all aspects of ownership of service providers and the way they offer their services. This will open up the market to innovative business models which were not possible before due to regulatory restrictions.
Globalization – Further globalization and a continuous trend of outsourcing professional services to emerging markets especially in the fields of compliance and other low value-added services.
Changing Client Demands – Changes in desires and the way clients buy their services. Corporate buyers increasingly focus on value, requiring fixed fees, and more transparency on pricing. Services are also being purchased via the à la carte model – choosing different providers for different tasks. Clients will also have access to more information enabling them to compare the cost of professional services, via online marketplaces for example, and search for alternative options more easily.
Search for jobs on our Job Board for the Professional Services Sector.
Technology and Artificial Intelligence – Historically, the professional services industry itself has shown a slow pace of implementing and adapting to technology changes while their clients and the rest of the world have shown to be less restrained. So, at some point, the industry needs to catch up on these developments. Technology and artificial intelligence will both be a substitute and complement for certain professional services and the impact will likely be more dramatic than anticipated. Highly complex tasks and processes will be simplified through technology; analyzing and research processes will be impacted; the use of all types of knowledge platforms, crowdsourcing models, and knowledge sharing models will be common practice.
It used to be thought that artificial intelligence is no substitute for judgment, the core business of professional advisors, but in fact, judgment is a response to uncertainty, and reducing uncertainty is something machines are very good at.
Role of Digital Technology and Artificial Intelligence
Because technology and artificial intelligence are the leading drivers for shaping the future state of the professional services industry it is good to focus a bit more on their role and trends that can be seen.
Overall, technology developments are both a possible threat to the professional services industry as well as an enabler to reinvent the way business is being done.
Key insights are:
- Increase in quality of services – Some of the technology threats can also be an opportunity to improve the way and the quality of services provided to clients because firms will increasingly use artificial intelligence and big data for their projects. As such, artificial intelligence and machine learning will be applied more and more to highly complex tasks, processes, and decisions in many fields including medicine, accounting, legal, and consulting. For example, the exponential growth in computing power combined with increasingly sophisticated approaches to artificial intelligence mean that systems like IBM’s Watson can potentially do the hard work of reading and analyzing vast amounts of legal opinions or medical research.
- Commoditization and automation – A continuous trend in professional services will be the evolvement from pure craftsmanship to standardization and then systematization and going forward it is very likely that technology developments will further speed up this process and may even be a game-changer. A side effect of technology commoditizing and automating more and more services is that there will be more highly specialized firms in services that cannot be commoditized or automated.
- From problem-solving towards preventative – Access to real-time data will move the advisory approach from problem-solving towards preventative as potential problems can be identified earlier in the process.
- Digital marketplaces for services – The rise of the new platform economy and related digital marketplaces will lead to the majority of professional services being sourced via online channels. It is expected that already by the end of 2017, almost half of the global workforce will exist of contingent workers, including independent contractors, SOW-based labor, and freelancers.
- More transparency – The ability to source services via online marketplaces and insights in expertise and talent becoming digitized, will lead to more transparency. This enables clients to find the right person for the job in a much simpler way and giving more control to clients.
- Knowledge sharing and platforms – Technology enables further externalization, meaning that certain professional services can be delivered equally well through commons production or free online platforms as the can through fee-based services. The further development and arrival of social networks for clients, with peer-to-peer advice and crowdsourcing mechanics, will further challenge the craftsmanship character of the industry.
- Increase in market reach – The increasing use of new technological communication methods will further extend the firm’s market reach and provide opportunities to connect with clients all over the world.
Clients of the Future
The needs of clients will also change and combined with the technology revolution it could be one of the main drivers that affect the way in which professional services will be delivered in the future.
Key insights are:
- Clients will increasingly use technology and automation for obtaining services and knowledge. This can be in the form of marketplaces for services, via knowledge sharing and crowdsourcing models or via virtual advisors backed by technology and artificial intelligence.
- Clients will insist on immediate results and look for price-competitive firms.
- The value of relationships will become more important and there will be more physical collaboration between clients and firms when possible but on the other hand, it will also be common practice that clients and advisors are located on different continents.
- Multidisciplinary teams will be built from multiple service providers to serve the needs of clients.
- The information gap between firms and clients will become much smaller because clients will be much better informed at a quicker pace.
- Clients will demand pricing based on outcome and value rather than hourly rates.
- Clients and firms will be more aligned in terms of principles, relationships, price-risk sharing, and business models.
- Clients will keep increasing their in-house capabilities, through acquiring highly specialized staff, improved processes, and more task automation opportunities.
- A Job Board with a 100% Professional Services focus.
- Search/post jobs in the Professional Services Sector.
- Submit your job to 150+ Job Boards with 1-click. Learn more.
How to Survive and Respond
Business Models of the Future
Predicting how the future firm will look is of course a very hard job. Will they look more like (software) platform companies than auditors? Will they be structured like networks? Will their organizational structure be very flexible in response to ever-changing client needs, pulling part of their resources from independent professionals and teams as needed?
Key insights in this respect are:
- Choose direction – Firms should make strategic choices with respect to services offered and geographic markets covered and four broad scenarios are possible:
- Take a step back and refine and refocus meaning scaling back on some existing markets/services.
- Keep things as is and stick to existing markets/services.
- Make some adjustments and looking into complementary markets/services.
- Go through a radical transformation and explore new markets/services. For existing firms, it will be much more difficult to have this radical transformation accompanied by a new business model so it will be much more likely that new players in the market will disrupt the status quo with new services and new business models.
- Continuous improving business models – Firms must improve their business models on a continuous basis which requires culture and mindset changes and very flexible organizational structures. When implementing new technologies, firms should think less, do more, be less risk-averse, and implement trial and error approaches.
- Value based fees – Firms will need to replace time-based fees with fixed and outcome-based fees and adopt lean and agile business models.
- Keep focussed on core – Certain processes should be outsourced to concentrate on that what you are best at, increasing value to clients.
- Determine talent strategy – Talent strategies of firms will be key in dealing with future challenges and the core model for the use and source for talent should change. As geographic borders will fade through emerging technology, firms must increasingly tap into internal and external mobile talent across markets and regions. In addition, the trend of both partners in a family having a professional career will continue. This will force firms to offer more “work-life integrations” because recruiting and retaining talent will become more competitive. Overall, future firms might have three talent pools:
- Partner and leaders that determine the culture in the firm.
- Traditional and permanent staff who are the primary fee earners who should be attracted, retained, and developed in the conventional way but taking into account the new circumstances.
- Non-traditional staff and external resources, including project managers, sales and marketing executives, dealmakers, data and technology experts as well as external fee earners. This staff can be accessed through partnership arrangements or contractor models and they require alternative incentives and training structures.
- Small multidisciplinary teams – Especially at the high end of the professional services industry it is likely that small multidisciplinary teams of entrepreneurial professionals who know how to get the most out of artificial intelligence systems will be able to deal with large and complex issues and service their clients.
- Ultimate direction – Richard Susskind, who is one of the leading authorities on “the future of professional services” has even said: traditional professional services continue to exist and enjoy the benefits of technology optimization and efficiencies, but are eventually displaced by that technology, ultimately leading to the dismantling of the professions.
Examples of Current New Business Models and Technology Applications
Examples of new technology applications, some of which already changed the name of the game, include:
- Private equity-backed commercial law firms challenging the traditional partner based law firms. New ownership models will likely be introduced and spread across all professional services.
- Other new business models applied to the legal market include Elevate, Conduit Law, and Lawyers on Demand. Access to legal services via membership type of models are also quickly rising across the world.
- The non-profit and online learning site Khan Academy has 10m unique users each month.
- Free online courses from Harvard University, HardvardX, received more sign-ups in one year than the entire historical attendance of university. And via edX , a growing community of over 7 million learners are connected to the best universities and institutions in the world.
- The medical advice site WebMD has serviced over 190m users since its incorporation and is only led by 100 nationwide doctors and health experts. The rise of a comparable site, devoted to the traditional professional services is just a matter of time and it is very likely that such a site already exists but just needs some more time to evolve and reach a critical mass.
- Auction site Ebay resolves 60m legal disputes per year via its Online Dispute Resolution software and the potential of Online Dispute Resolution mechanics looks very promising.
- Huffington Post reached more subscribers in 6 years than the New York Times which is 164 years old.
- Wikistrat has brought an entirely different approach to solving clients’ problems as it crowdsources solutions through an online global network of more than 2,000 small and medium-sized businesses.
- Lex Machina and KIM are examples of automated standalone legal services based on information technology and artificial intelligence.
- Freelancer sites like Upwork, Freelancer, People Per Hour, and many more global players have already commoditized part of the professional services freelancing work and have connected millions of professionals in for example India with clients in the US, at the same time putting enormous pressure on freelancer’s hourly rates.
- New online accounting platforms are emerging as we speak, some of which have substantial online communities to support them. For example over 48m US citizens submit tax returns using TurboTax supported by a huge community of people who can give advice.
Consultants 500 – Connecting Businesses with Professional Services Industry
A recent study from McKinsey stated that digital talent platforms are set to revolutionize business and up to 540 million individuals could benefit from online talent platforms by 2025. These platforms have the greatest potential for high-tech and high-end professional service firms, both depending on specialized, expensive, and hard-to-find pro’s.
Businesses looking for advisors typically use the following channels to find the best person for the job: Web Search (75%), Service Provider Websites (73%), Events/Seminars (54%), Peer Recommendations (54%), Online Associations (42%), Media Publications (38%) and Social Media and Blogs (35%).
From the above, it can be concluded that the internet is by far the leading channel for finding your ideal advisor. However, the internet is literally loaded with millions of advisors who say they can deliver exactly what you need. The problem is how to find and be found in a quick and easy way.
Ideally, you create a shortlist of advisors that meet your demands, compare them, select the best one for the job, and that only within a few minutes. Our online platform, Consultants 500, is just the tool for that! Via our marketplace, you can search for the following typical services provided by the professional services industry: Accounting, Consulting, Legal, Tax, Marketing, Web Design, Recruiting, Writing & Translation, and Design.
We are getting ready for the future and we make the advisory world more transparent by sharing advisor’s specialization, their work, and their clients’ feedback. 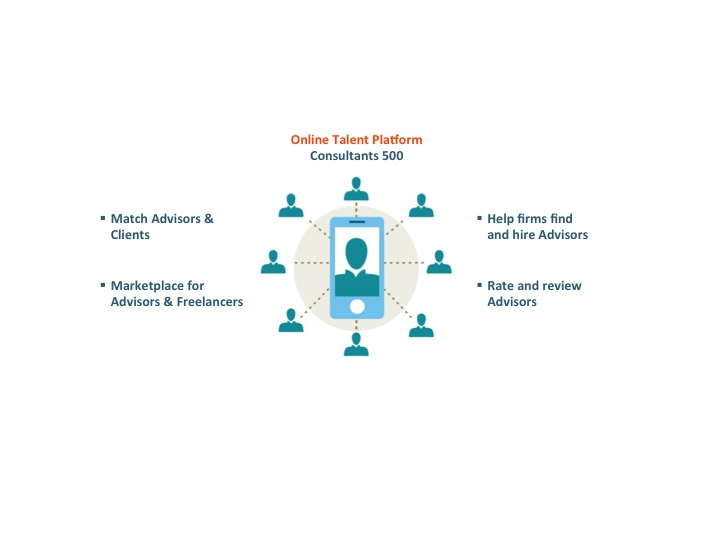
Create profiles, find business consultants, rate & review work done!
Resources
This article was written by Rufus Franck, the founder of Consultants 500, and I have over 16 years of experience working in the professional services industry. There are several reasons why I founded Consultants 500, but one of these reasons is my strong belief that the professional services industry is at the gates of a digital transformation process.
It is very difficult to highlight all the sources used for this article because it is a combination of knowledge obtained during my career in the professional services industry and many articles and studies read during the process of starting the Consultants 500 platform. But if you just search for “the future of” on google, you will see that there are a lot of like-minded out there in the world.
Consultants 500
Via our two platforms, you can find jobs, professional services providers, and more in the professional services sector, like the accounting, legal, consulting, web design and marketing industry.
- Search for Jobs, Professional Services, and more in the Professional Services industry.
- Fine-tune your search to fulfill your needs and directly contact each other.
- Get more relevant results due to a 100% Professional Services focus.
- Search for jobs in the Professional Services sector only.
- Browse by Professional Services industry, firm, country, city, salary, and more.
- Find your dream job now!
- Search for the most commonly used Professional Service providers in the Professional Services industry.
- Fine-tune your search to fulfill your needs.
- Directly contact each other.
- Get the job done.
Follow Us